Featured Publications
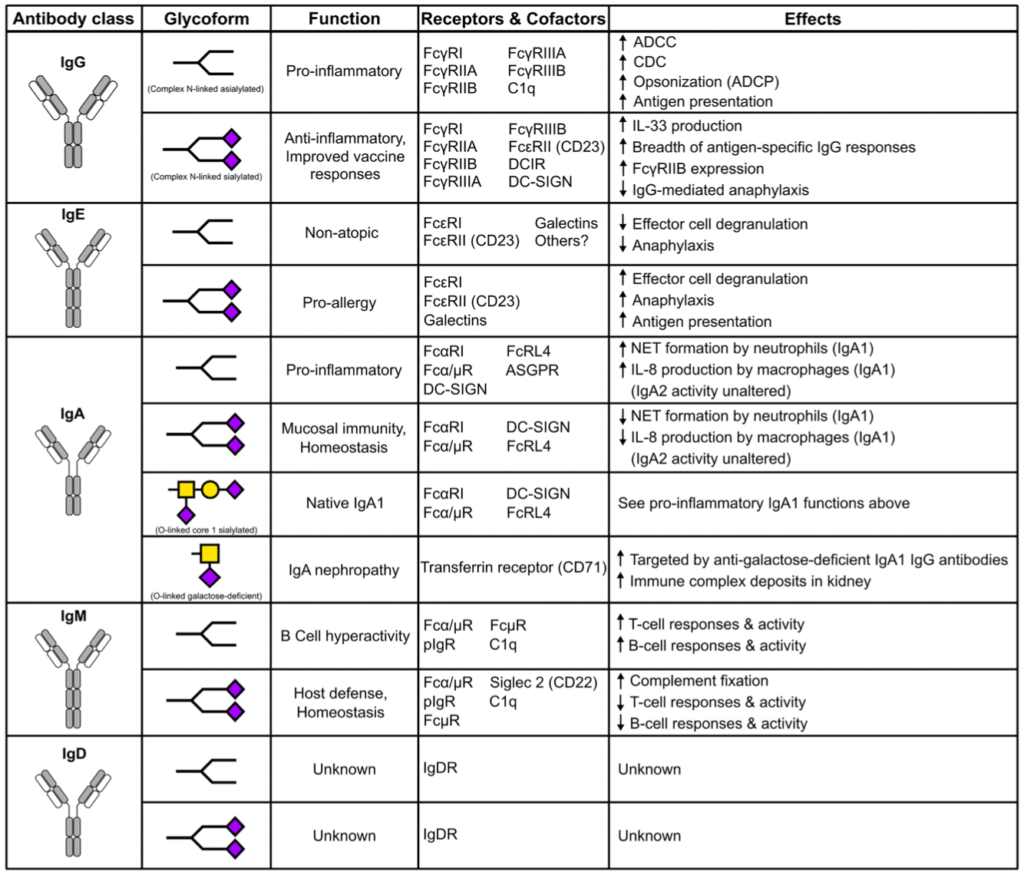
Sialylation as an Important Regulator of Antibody Functionality
Ravi Vattepu, Sunny L. Sneed, and Robert M. Anthony. Frontiers in Immunology March 17, 2022; DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.818736. Epub 2022 March 17.
Summary
Antibodies play a critical role in linking the adaptive immune response to the innate immune system. In humans, antibodies are categorized into five classes, IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD, based on constant region sequence, structure, and tropism. In serum, IgG is the most abundant antibody, comprising 75% of antibodies in circulation, followed by IgA at 15%, IgM at 10%, and IgD and IgE are the least abundant. All human antibody classes are post-translationally modified by sugars through glycosylation. The resulting glycans take on many divergent structures and can be attached in N-linked and O-linked glycans, and are distinct by antibody class, and by position on each antibody. Many of these glycan structures on antibodies are capped by sialic acid. It is well established that the composition of the N-linked glycans on IgG exert a profound influence on its effector functions. However, recent studies have described the influence of glycans, particularly sialic acid for other antibody classes. Here, we discuss the role of glycosylation, with a focus on terminal sialylation, in the biology and function across all antibody classes. Sialylation has been shown to influence not only IgG, but IgE, IgM, and IgA biology, making it an important and unappreciated regulator of antibody function.
Modulating T Follicular Cells In Vivo Enhances Antigen-Specific Humoral Immunity
Jose D. Pagan, Hera Vlamakis, Anthony Gaca, Ramnik J. Xavier and Robert M. Anthony. J Immunol May 19, 2021, ji2001434; DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2001434. Epub 2021 May 19. PubMed
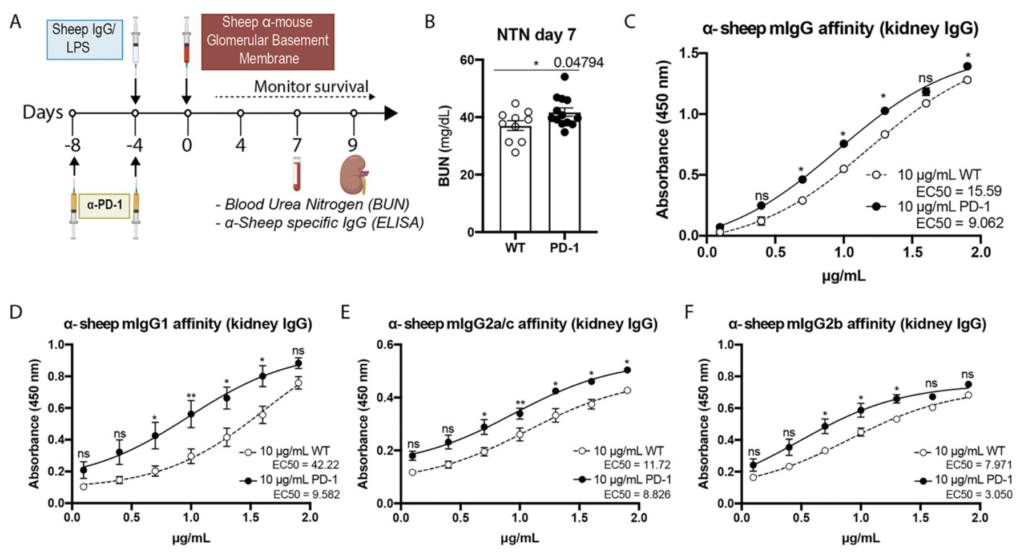
Summary
Generation of high-affinity IgG is essential for defense against infections and cancer, which is the intended consequence of many vaccines, but can cause autoimmune and inflammatory diseases when inappropriately directed against self. The interplay of T follicular helper (TFH) cells and T follicular regulatory (TFR) cells is critical for the production of high-affinity IgG of a specific subclass. In this study, we sought to improve Ag-specific IgG responses with two interventions intended to transiently diminish TFR cell influence. First, adult mice were administered an antibiotic mixture (ABX) for an extended period to deplete the immunoregulatory intestinal microbiota. This intriguingly increased TFH cell and reduced TFR cell numbers. 2,4,6-Trinitrophenyl hapten conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin immunization resulted in higher affinity 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl hapten–specific IgG1 in ABX mice compared with controls. In a model of IgG-driven inflammatory nephritis, ABX mice had significantly worse nephritis accompanied by higher affinity Ag-specific IgG2b and enriched TFH cells compared with controls. Second, we sought to functionally manipulate TFH and TFR cells, which both express the checkpoint inhibitory molecule, PD-1, by administration of anti–PD-1 during immunization. This intervention enhanced the affinity of Ag-specific IgG of the appropriate subclass and increased in TFH cells following 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl hapten conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin immunization and nephritis induction. These results suggest that altering TFH and TFR cell ratios during immunization is an appealing strategy to qualitatively improve Ag- and subclass-specific IgG responses.
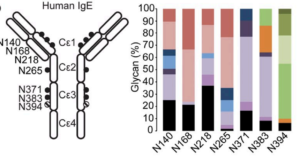
Sialylation of immunoglobulin E is a determinant of allergic pathogenicity
Kai-Ting C. Shade, Michelle E. Conroy, Nathaniel Washburn, Maya Kitaoka, Daniel J. Huynh, Emma Laprise, Sarita Patil, Wayne Shreffler, Robert M. Anthony. Nature. 2020 Jun;582(7811):265-270. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2311-z. Epub 2020 May 20. PubMed
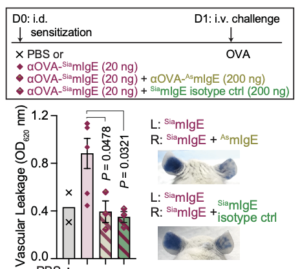
Summary
Approximately one-third of the world’s population suffers from allergies1. Allergen exposure crosslinks mast cell- and basophil-bound immunoglobulin E (IgE), triggering the release of inflammatory mediators, including histamine2. Although IgE is absolutely required for allergies, it is not understood why total and allergen-specific IgE concentrations do not reproducibly correlate with allergic disease3-5. It is well-established that glycosylation of IgG dictates its effector function and has disease-specific patterns. However, whether IgE glycans differ in disease states or impact biological activity is completely unknown6. We therefore unbiasedly examined glycosylation patterns of total IgE from peanut-allergic and non-atopic individuals. This revealed an increase in sialic acid content on total IgE from peanut-allergic individuals compared to non-atopic subjects. Sialic acid removal from IgE attenuated effector cell degranulation and anaphylaxis in multiple functional models of allergic disease. Therapeutic interventions, including sialic acid removal from cell-bound IgE with a FcεRI targeted-neuraminidase, or administration of asialylated IgE, markedly reduced anaphylaxis. Together, these results establish IgE glycosylation, and specifically sialylation, as an important regulator of allergic disease.
Media Coverage
- Massachusetts General Hospital. “New insight into allergies could improve diagnosis and treatment.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 20 May 2020. Link to the article
- FARE BLOG. Molecule Identified in Study May Influence Allergies and Reaction Symptoms Findings from a FARE Investigator may aid the search for food allergy treatments and improved diagnostic tests. Link to the article
- The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. News Beyond Our Pages. Marc E. Rothenberg, MD, PhD ∗ Jean Bousquet, MD ∗ DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.014. Link to the article
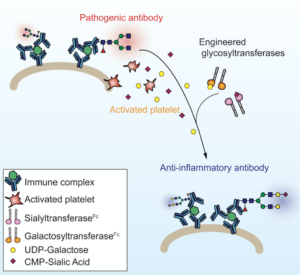
Engineered Sialylation of Pathogenic Antibodies In Vivo Attenuates Autoimmune Disease.
Pagan JD, Kitaoka M, Anthony RM. Cell. 2018 Jan 25;172(3):564-577.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.041. Epub 2017 Dec 21.PubMed
Summary
Self-reactive IgGs contribute to the pathology of autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Paradoxically, IgGs are used to treat inflammatory diseases in the form of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Distinct glycoforms on the IgG crystallizable fragment (Fc) dictate these divergent functions. IgG anti-inflammatory activity is attributed to sialylation of the Fc glycan. We therefore sought to convert endogenous IgG to anti-inflammatory mediators in vivo by engineering solubilized glycosyltransferases that attach galactose or sialic acid. When both enzymes were administered in a prophylactic or therapeutic fashion, autoimmune inflammation was markedly attenuated in vivo. The enzymes worked through a similar pathway to IVIG, requiring DC-SIGN, STAT6 signaling, and FcγRIIB. Importantly, sialylation was highly specific to pathogenic IgG at the site of inflammation, driven by local platelet release of nucleotide-sugar donors. These results underscore the therapeutic potential of glycoengineering in vivo.
Media Coverage
- Massachusetts General Hospital. “Anti-inflammatory antibodies may treat autoimmune disease: Enzyme treatment converts autoantibodies into anti-inflammatory antibodies in animal models of two autoimmune diseases.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 21 December 2017. Link to the article
- GEN: Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News
“Technique Converts Harmful Autoantibodies into Anti-Inflammatory Antibodies In Vivo.” Link to the article - Nature reviews rheumatology volume 14, page121(2018). Research Highlight.
“Glycoengineering has therapeutic potential”Link to the article
A single glycan on IgE is indispensable for initiation of anaphylaxis.
Shade KT, Platzer B, Washburn N, Mani V, Bartsch YC, Conroy M, Pagan JD, Bosques C, Mempel TR, Fiebiger E, Anthony RM. J Exp Med. 2015 Apr 6;212(4):457-67. doi: 10.1084/jem.20142182. Epub 2015 Mar 30.PubMed
Summary
Immunoglobulin ε (IgE) antibodies are the primary mediators of allergic diseases, which affect more than 1 in 10 individuals worldwide. IgE specific for innocuous environmental antigens, or allergens, binds and sensitizes tissue-resident mast cells expressing the high-affinity IgE receptor, FcεRI. Subsequent allergen exposure cross-links mast cell-bound IgE, resulting in the release of inflammatory mediators and initiation of the allergic cascade. It is well established that precise glycosylation patterns exert profound effects on the biological activity of IgG. However, the contribution of glycosylation to IgE biology is less clear. Here, we demonstrate an absolute requirement for IgE glycosylation in allergic reactions. The obligatory glycan was mapped to a single N-linked oligomannose structure in the constant domain 3 (Cε3) of IgE, at asparagine-394 (N394) in human IgE and N384 in mouse. Genetic disruption of the site or enzymatic removal of the oligomannose glycan altered IgE secondary structure and abrogated IgE binding to FcεRI, rendering IgE incapable of eliciting mast cell degranulation, thereby preventing anaphylaxis. These results underscore an unappreciated and essential requirement of glycosylation in IgE biology.
Media Coverage
- JEM: Journal of Experimental Medicine. Insights. April 06 2015. Breaking the allergic response by disrupting antibody glycosylation. Link to the article
Other Anthony Publications and Collaborations
Lung injury induces a polarized immune response by self antigen-specific Foxp3+ regulatory T cells
Daniel S. Shin, Sneha Ratnapriya, Creel Ng Cashin, Lucy F. Kuhn, Rod A. Rahimi, Robert M. Anthony, and James J. Moon. bioRxiv. 2023 Feb 10. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.09.527896. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.02.09.527896v1.full
Epigenetic reader SP140 loss of function drives Crohn’s disease due to uncontrolled macrophage topoisomerases
Hajera Amatullah, Isabella Fraschilla, Sreehaas Digumarthi, Julie Huang, Fatemeh Adiliaghdam, Gracia Bonilla, Lai Ping Wong, Marie-Eve Rivard, Claudine Beauchamp, Virginie Mercier, Philippe Goyette, Ruslan I Sadreyev, Robert M Anthony, John D Rioux, & Kate L Jeffrey. Cell. 2022 Aug 18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.048. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35952671/
IgE Glycosylation in Health and Disease
Kai-Ting Shade, Michelle Conroy, & Robert M Anthony. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Mar 1. doi: 10.1007/82_2019_151. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30820668/
Cis interaction between sialylated FcγRIIA and the αI-domain of Mac-1 limits antibody-mediated neutrophil recruitment
Gurpanna Saggu, Koshu Okubo, Yunfeng Chen, Ravi Vattepu, Naotake Tsuboi, Florencia Rosetti, Xavier Cullere, Nathaniel Washburn, Suhail Tahir, Aaron M. Rosado, Steven M. Holland, Robert M. Anthony, Mehmet Sen, Cheng Zhu, and Tanya N. Mayadas. Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 29. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07506-1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6265255/
Modulation of Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice by Gut Microbiota Through Mucosal Inflammation and Autoantibody Generation
Widian K Jubair, Jason D Hendrickson, Erin L Severs, Hanna M Schulz, Sumitra Adhikari, Diana Ir, Jose D Pagan, Robert M Anthony, Charles E Robertson, Daniel N Frank, Nirmal K Banda, & Kristine A Kuhn. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Jul 2. doi: 10.1002/art.40490. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29534332/
Maintenance of macrophage transcriptional programs and intestinal homeostasis by epigenetic reader SP140
Stuti Mehta, D Alexander Cronkite, Megha Basavappa, Tahnee L Saunders, Fatemeh Adiliaghdam, Hajera Amatullah, Sara A Morrison, Jose D Pagan, Robert M Anthony, Pierre Tonnerre, Georg M Lauer, James C Lee, Sreehaas Digumarthi, Lorena Pantano, Shannan J Ho Sui, Fei Ji, Ruslan Sadreyev, Chan Zhou, Alan C Mullen, Vinod Kumar, Yang Li, Cisca Wijmenga, Ramnik J Xavier, Terry K Means, & Kate L Jeffrey. Sci Immunol. 2017 Mar 3. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aag3160. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28783698/
In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy
Sean P Arlauckas, Christopher S Garris, Rainer H Kohler, Maya Kitaoka, Michael F Cuccarese, Katherine S Yang, Miles A Miller, Jonathan C Carlson, Gordon J Freeman, Robert M Anthony, Ralph Weissleder, & Mikael J Pittet. Sci Transl Med. 2017 May 10. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28490665/
Dual action of neurokinin-1 antagonists on Mas-related GPCRs
Ehsan Azimi, Vemuri B Reddy, Kai-Ting C Shade, Robert M Anthony, Sebastien Talbot, Paula Juliana Seadi Pereira, & Ethan A Lerner. JCI Insight. 2016 Oct 6. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89362. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27734033/
IgE/FcεRI-Mediated Antigen Cross-Presentation by Dendritic Cells Enhances Anti-Tumor Immune Responses
Barbara Platzer, Kutlu G Elpek, Viviana Cremasco, Kristi Baker, Madeleine M Stout, Cornelia Schultz, Eleonora Dehlink, Kai-Ting C Shade, Robert M Anthony, Richard S Blumberg, Shannon J Turley, & Edda Fiebiger. Cell Rep. 2015 Mar 10. doi: 0.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.015. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25753415/
Acute inflammation primes myeloid effector cells for anti-inflammatory STAT6 signaling
Fredrik Wermeling, Robert M Anthony, Frank Brombacher, & Jeffrey V Ravetch. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013 Aug 13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312525110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23898202/
Intravenous gammaglobulin suppresses inflammation through a novel Th2 pathway.
Robert M. Anthony , Toshihiko Kobayashi , Fredrik Wermeling , and Jeffrey V. Ravetch. Nature. 2011 Jun 19;475(7354):110-3. doi: 10.1038/nature10134.
Identification of a receptor required for the anti-inflammatory activity of IVIG
Robert M. Anthony, Fredrik Wermeling, Mikael C. I. Karlsson, and Jeffrey V. Ravetch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 16;105(50):19571-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810163105. Epub 2008 Nov 26.
Recapitulation of IVIG Anti-Inflammatory Activity with a Recombinant IgG Fc
Anthony RM, Nimmerjahn F, Ashline DJ, Reinhold VN, Paulson JC, Ravetch JV. Science. 2008 Apr 18;320(5874):373-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1154315.
Agalactosylated IgG antibodies depend on cellular Fc receptors for in vivo activity
Falk Nimmerjahn, Robert M. Anthony, and Jeffrey V. Ravetch. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 15;104(20):8433-7. Epub 2007 May 7